
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODY SYNDROME
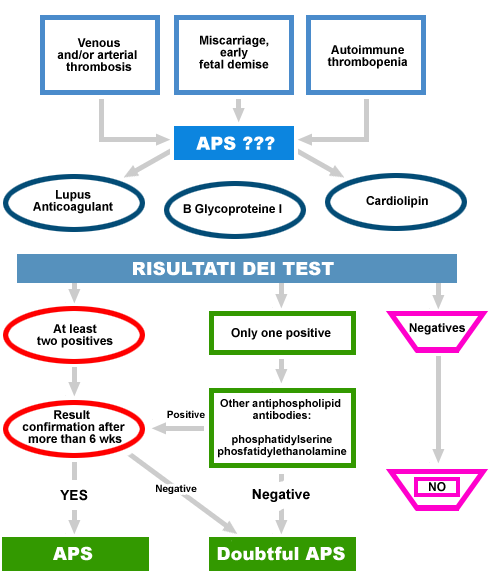
The interest in anti-phospholipid antibodies stems from observing their association with peculiar clinical manifestations such as venous and arterial thrombosis, thrombocytopenia and recurrent miscarriages. As a whole, such manifestations are described as antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS).
In this context, antiphospholipid antibodies are directed against plasma proteins bound to anionic phospholipid surfaces.
In theory, a primitive form (PAPS) can be identified when an isolated phenomenon arises, whereas a secondary form (secondary APS) is observed within the framework a systemic autoimmune disease, mainly Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) or its variants such as Discoid Lupus, Subacute Cutaneous Lupus (positive anti-Ro) and Sjögren’s syndrome.
The antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome is an autoimmune disorder. Thus, finding autoantibodies other than aPL and with a different prevalence in the serum of patients with APS is not surprising.
The presence of anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL) has been regarded as the typical serologic marker of the syndrome, although it became immediately evident that these antibodies could not only recognize cardiolipin, but the whole phospholipid family with a negative electric charge.
Details of the single phospholipids playing an important role in APS diagnosis are given below.
| FREQUENCY OF THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME | |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | 35% |
| Venous thrombosis | 24% |
| Stroke | 6-29% |
| Coronary disease | 3-80% |
| Idiopathic abortion | 10-20% |
ANTI CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES (aCL)
The binding of highly purified aCL antibodies requires a serum or plasma component. The component in question, called cardiolipin co-factor, is identified in β2 glycoprotein I. The knowledge acquired in the past few years has shown how the so-called anti-phospholipid antibodies are mostly directed not against the phospholipids themselves, but rather against the proteins that bind phospholipids (e.g.: β 2GPI, prothrombin, etc.). In particular, β2 glycoprotein I has been recognized as the main part of the antigenic complex detected by anti-cardiolipin antibodies.
ANTI β2 GLICOPROTEIN ANTIBODIES
Today, anti β2 GPI antibodies play a more specific and more sensitive diagnostic role than the classic anti-cardiolipin antibody test, for different reasons:
- It binds phospholipids with negative electric charge.
- It is abundantly present in the serum of all mammals and, therefore, also in bovine serum which is widely used in ELISA assays for the detection of aCLs.
- β2GPI is a lipoprotein and, by binding to the phospholipids, it modifies their structure from lamellar to hexagonal. This change may be important, since the hexagonal form has been demonstrated to have greater antigenic properties.
- Finally, β2GPI is a natural anticoagulant and its possible inactivation by an antibody reaction could lead to an increase of thrombotic events, as observed in patients affected by the syndrome.
The antiphospholipid antibodies deriving from the serum of patients with an autoimmune disease react better when ß2GPI is present.
A patient with clinical suspicion of APS and anti-beta2GPI antibodies is very likely to suffer from the syndrome, even in the presence of LAC or aCL positivity.
ANTI PROTHROMBIN ANTIBODIES
Prothrombin (factor II), a vitamin-K dependent glycoprotein, is activated into thrombin in the coagulation cascade.
Only anti-prothrombin antibodies that recognize the prothrombin and phosphatidylserine complex are correlated with lupus anticoagulant and the clinical manifestations of APS.
Recently, evidence was found that SLE patients with a positive titer of anti-prothrombin antibodies run a greater risk of developing arterial and venous thrombosis. Anti-prothrombin antibodies were also described as a risk factor for cardiac infarction.
Anti-prothrombin antibodies are closely associated to a tendency to miscarry in patients with APS.
Anti-prothrombin antibodies are reported to be the most sensitive indicator antibodies in the determination of the tendency to miscarry in APS, in comparison with other phospholipid antibodies.
If anticoagulant lupus and antiphospholipid antibodies are also present, the risk of thrombosis considerably increases and is, furthermore, influenced by the magnitude of antibody titer. As the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies can also be transitory, positivity should be checked by repeating the test after 3 months.
- 7600 Eu-ACA G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti cardiolipin - 7601 Eu-ACA A
EIA for the detection of IgA autoantibodies anti cardiolipin - 7602 Eu-ACA S
EIA for the detection of IgGAM autoantibodies anti cardiolipin - 7603 Eu-BGPI G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti beta-2-glycoprotein I (B2GPI) - 7604 Eu-BGPI A
EIA for the detection of IgA autoantibodies anti beta-2-glycoprotein I (B2GPI) - 7605 Eu-BGPI S
EIA for the detection of IgGAM autoantibodies anti beta-2-glycoprotein I (B2GPI) - 7606 Eu-PS S G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti phospholipid antigens (Cardiolipin, Phosphatidyl Serine, Phosphatidyl Inositol, Phosphatidic Acid and b-2-Glycoprotein I) - 7607 Eu-Pserin G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti phospatidyl serine - 7608 Eu-Pinositol G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti phosphatidyl inositol - 7609 Eu-Pacid G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti phosphatidic acid - 7610 Eu-Prothrombin G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti prothrombin - 7611 Eu-Prothrombin A
EIA for the detection of IgA autoantibodies anti prothrombin - 7612 Eu-Prothrombin S
EIA for the detection of IgGAM autoantibodies anti prothrombin - 7613 Eu-7 APS Pr
EIA for simultaneous and differentiated detection of autoantibodies IgG and IgM anti phospholipidis antigens (1 B2GPI, 2 Cardiolipin/B2GPI, 3 Phosphatidyl Serine/B2GPI, 4 Phosphatidyl Inositol/B2GPI, 5 Phosphatidic Acid/B2GPI, 6 all antigens simultaneous with B2GPI and 7 all antigens simultaneous without B2GPI) - 7669 Eu-Annexin G/M
EIA for the detection of IgG and IgM autoantibodies anti annexin V

